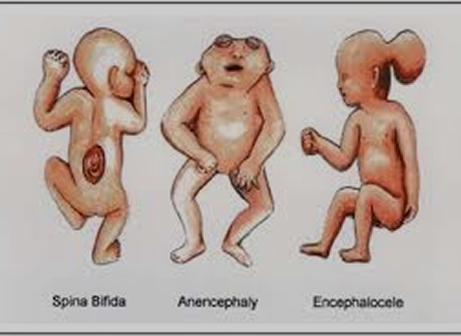
Any deviation from normal vasculature in human body during developmental process
The exact cause for this defect is often unknown. The probable causes are-
- Genetic inheritance (Paternal or maternal): Father or Mother either parent can pass on a gene or genes that cause clefts problems.
- Chromosomal cause.
- Environmental pollutions
- Medicines and chemicals during pregnancy
- Phenytoin
- Phenobarbital
- Sodium valproate
- Benzodiazepines
- Pain killers
- Traditional Medicines like different herbals , Homeopathic medicines, etc
Diseases of mother during pregnancy like-
- Diabetes,
- Hypertension,
- Viral infections,
- Bacterial disease etc
Maternal nutrition during pregnancy
- Malnutrition
- Obesity
- Lack of Vitamins and minerals like
- Folic acid
- Vitamin B complexes
- Sodium valproate
- Iron
- Zinc, etc
Radiations during pregnancy
Exposure to various intoxication of parents even before pregnancy
- Alcohol
- Tobacco
- Others
Age of parents (Both early/late paternal and maternal age)
Consanguinity ( Parents are cousin /close blood relatives of each other)
Psychological upset of mother during pregnancy. etc.
In some cases it may be an indicator of other more serious underlying conditions, such as testicular cancer.
So, always check with your doctor before using any medication or supplement while you are pregnant
- Treatments for birth defects vary by disorder. For details visit this website and contact with us for more information about treatments of birth defects.
- Any children may become ill or injured at one time or another. Most problems are simple and can be solved by your pediatrician. At times, however, special care from a pediatric plastic surgeon may be needed and may make the difference in achieving the best possible cosmetic result. If you think your child needs this kind of special care, request a visit with us. If your child needs surgery to fix a deformity caused by a birth defect, injury, physical deformity, or tumor, a pediatric plastic surgeon has the experience and qualifications to treat your child.
- Children are not just small adults.They differ significantly from each other and from adults both in physiologic and anatomic organ system as well as their psychological system.They cannot always say what is bothering them. They cannot always answer medical questions, and are not always able to be cooperative during a medical examination.
- So, children have to deal in a way that makes them relaxed and cooperative
Sometimes these need to multi disciplinary team approach and I do this.
Epigastric Hernia: Reducible swelling on abdomen any where in midline above umbilicus. It will gradually increase in size. Though it is not problematic initially, it will be pain full and will be problematic with time.
Treatment: Surgical.
Umbilical hernia: Congenital hernia (reducible swelling) through umbilicus. It becomes more prominent when the child cries. Most of the umbilical hernia does not need any treatment; they are cured naturally within 5-6 years of life. If they persist or become problematic, they must be treated by surgery.
Para umbilical hernia: Hernia (reducible swelling) around the umbilicus. Usually it appears when the child cries. Treatment is surgery.
Inguinal Hernia: Hernia (reducible swelling) at inguinal region. Usually it appears when the child cries. Treatment is emergency surgery, otherwise it may become life threatening at any time.
Exomphalous: Congenital defects in umbilicus. Some may need emergency surgery.
Gastroschrisis: Congenital defect in umbilicus, through which abdominal organs come out. This is a life threatening condition. Child may not survive. Treatment is emergency surgery.
Bladder exstrophy-Epispadias complex:
Congenital defect of urinary bladder and lower abdomen, with or without genital defect. Anterior wall of urinary bladder and lower abdominal wall was not formed. As a result urinary bladder exposed and urine always comes out. There may be associated external genital problems. These patients are socially unacceptable for their foul smell of urine. Their conjugal life will be hampered also. Preferable treatment is surgical correction within 48 hours of life
Syndactyly: Variable fusion of one or more adjacent fingers.
Treatment: Surgical Correction.
Apert’s Syndrome: Is the combination of craniofacial deformity with complex syndactyly of hands and feet.
Treatment: Surgical Correction.
Polydactyly: Extra digit of hands and feet.
Mirror Hand : Symmetrical duplication of limb at midline. Fingers are paired on that hand. There are 6 or 8 symmetrical fingers.
Brachydactyly : Short fingers
Cleft Hand : V-Shaped cleft in the center of the hand
Absence of the fingers:
Treatment: Finger transplantation/ Artificial finger
- Symbrachydactyly : Fused short fingers Clinodactyly : Angulations’ of digit in the radioulnar plane more than 100° . Camptodactyly : Painless flexor contracture of proximal interphalangial (PIP) joint. Macrodactyly : Enlargement of one or more fingers and toes. Club hand : Deformity of hand and forearm. Arthrogyphosis: Congenital joint contracture. Club foot: It is a congenital deformity involving one foot or both. Though all congenital deformity of foot once called club foot but now a day congenital talipes equinovarus (CTEV) is called club foot. The affected foot looks like it has been rotated internally at the ankle. Without treatment, people with club feet often appear to walk on their ankles or on the sides of their feet. It is a relatively common birth defect. It occurs in males twice as frequently as in females.
- Diagnosis: Clinical. No investigations needed for diagnosis. X-ray needed to see the extension of diseases. Treatment: Depends upon the age of the child. Before the age of one year serial casting (Plaster) by Ponseti method may be or may not be followed by simple operation (Tenotomy). Surgical treatment – if the child visits the doctor after his/her one year of age.
- Each case is different, but in most cases extensive surgery is not needed to treat clubfoot. Congenital dislocation of Hip: One or both hip joint may be displaced during birth process, which should be properly treated soon after diagnosis otherwise child will be crippled. Congenital genu recurvatum, genu varus(bow knees/ Blount’s Disease): Lower limb may develop bow like either inward or out ward. With development/growth of child these may cured naturally. A mild case does not need any treatment. Sometimes these may need surgical correction. Congenital Pseudoarthrosis of tibia: Leg may be angulated congenitally like a false joint. Treatment: Surgical correction as early as possible.
Cleft Foot: V-Shaped cleft in the center of the foot. Treatment of Limb Anomalies: Almost all congenital limb anomalies need surgical correction. Some may not need surgery like club foot if attend neonatal period.
- It is said ‘Misfortunes never come singly’. It is true in case of oro-facial clefts. There may be associated congenital heart diseases, defects in limbs, ear and other birth defects
To diagnose any birth defects, we have to check natural orifices of new born like Mouth cavity, Ear, Nose, Genitalia, Anal orifice. Cleft lip and facial clefts are externally visible defects.
We may do some investigations like Echocardiography, Complete Blood Count, BT, CT, CXR, etc. in suspected patients and for evaluation of fitness for operation.
- Looks ugly-Social, Psychological, educational problem. Peoples try to avoid social relationship with these families.
- Feeding difficulties- Malnutrition.
- Frequent respiratory tract infections like pneumonia which endangers life.
- Ear infection –hearing probblem.
- Speech problem.
- Dental problem.
- Economical problem of family and later of him/herself.
- Untimely death.
Treatment is operation for any kinds of oro-facial clefts if patient is fit for operation. So, such baby should be under supervision of a cleft surgeon just from birth. Surgeon will guide the parents how to feed, how to take care of baby.
- Lip: Treatment at an early age (If possible within one month of age) gives better result if child is fit for operation. But it can be repaired at any age. We usually do it at the age 3 months or more.
- Palate: 6-12 months of age for best speech out come. But can operate in any age, there will be improvement of speech.
- Cleft Nose repair and correction of Secondary deformities of Repaired Clefts: 4-5 years
- Gum : Alveolar Bone Graft. 2-5 years (alloplastic Bone graft), 5-8 years (Autologus bone graft)
From the age of 3 years, but can be given earlier along with behavioral therapy if needed.
1. www.who.int › genomics › anomalies/en : International Collaborative Research on Craniofacial Anomalies
2. Interrante JD, Ailes EC, Lind JN, Anderka M, Feldkamp ML, Werler MM, Broussard CS. (2017). Risk comparison for prenatal use of analgesics and selected birth defects, National Birth Defects Prevention Study 1997–2011. Annals of Epidemiology; 27(10), 645–653.
3. Saeed BO, Moore MG, Zawahrah H, Tayem M, Kavoosi T & van Aalst JA. (2019). The Influence of Consanguinity on Familial Clefting Among Palestinians. The Cleft Palate-Craniofacial Journal; 56 ( 8), 1072-1079
4. https://www.clapa.com/
5. Rejeev BR, Prasad KVV, Shetty PJ, Preet (2017). The relationship between orofacial clefts and consanguineous marriages: A hospital register-based study in Dharwad, South India. Journal of Cleft Lip Palate and Craniofacial Anomalies ;4(1):3-8.
6. Bille C, Skytthe A , Vach W, Knudsen LB , Andersen AM, Murrary JC and Christensen K. (2005). Parent’s Age and the Risk of Oral Clefts. Epidemiology; 16(3): 311–316
7. Chuang CH, Doyle PE, Wang JD, Chen PC, Lai JN, Chang PJ (2006). Herbal medicines used during the first trimester and major congenital malformations: an analysis of data from a pregnancy cohort study. Drug Saf ; 29(6):537-48,
